Vitiligo is a skin condition that is characterised by patches of lighter skin that form due to loss of pigment. These patches are caused by the destruction of melanin, the pigment that gives skin its colour.
Vitiligo can affect any part of the body, but it is most commonly seen on the face, neck, hands, feet and arms.
The cause of vitiligo is unknown, but it is believed to be an autoimmune disorder.
Treatment can include topical steroids, light therapy and medications that help restore pigment to the affected areas.
It is important to remember that while vitiligo can be disfiguring, it is not contagious and does not cause any physical pain. With proper treatment, the affected areas may return to their normal colour.
Types of Vitiligo
There are two main types of vitiligo: segmental vitiligo and non-segmental vitiligo.
Segmental vitiligo is characterised by patches of depigmentation that typically appear on one side of the body.
Non-segmental vitiligo, on the other hand, is characterised by symmetrical patches that generally appear on both sides of the body.
In addition to these two main types, there is also a rare form of vitiligo known as universal vitiligo, which affects nearly all of the body’s skin and hair.
Symptoms
Some of the most common symptoms of vitiligo include:
If you experience any of these symptoms, seek the help of your dermatologist at the earliest.
Early diagnosis and treatment can greatly help reduce the appearance of vitiligo and prevent further loss of skin colour.
Causes
While the exact cause of vitiligo is unknown, there are several potential causes that have been identified. These include:
Genetic predisposition: It may be caused by an inherited genetic mutation that affects the melanin-producing cells.
Autoimmune disorders: It may be triggered by an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys its own healthy cells.
Sunburn: Long-term sun exposure can damage the melanin-producing cells, leading to the development of white patches.
Stress: Stress can weaken the immune system and cause skin damage, which may lead to the condition.
Exposure to certain chemicals: Exposure to certain chemicals, such as industrial dyes or bleach, can damage the melanin-producing cells and lead to vitiligo.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of vitiligo involves a physical exam and a review of the your’s medical history.
Your doctor will look for signs of skin discolouration and examine any areas of discolouration for signs of inflammation or infection.
A skin biopsy may also be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Additional tests, such as blood work for rule out any autoimmune response to the condition and an eye exam, may also be ordered to rule out other conditions.
Treatment and Management
The most common treatment option is topical medication, such as corticosteroid creams or ointments that are applied directly to the affected area.
Other options include light therapy, phototherapy and laser treatments.
For more severe cases, surgery may be recommended to transplant skin cells from unaffected areas to the areas affected by vitiligo.
It’s always important to consult your doctor for advice about the best treatment for your particular condition.
Can Vitiligo be Prevented?
While there is no surefire way to prevent vitiligo, there are some steps you can take to reduce your risk.
First, it is important to take care of your skin by wearing sunscreen and avoiding excessive sun exposure, which can trigger vitiligo.
Also, it is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle by eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly and avoiding smoking and alcohol.
Stress can also increase the risk of vitiligo, so it is important to manage stress levels through relaxation exercises such as yoga and pranayama.
If you have a family history of vitiligo, you may want to speak with your doctor about monitoring your skin for any changes.
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent vitiligo, these steps may help reduce your risk.
Is There a Diet for Vitiligo?
There is no vitiligo diet as such which can be recommended, but there are a few that might help according to popular evidence.
If at all, a healthy diet for vitiligo should include plenty of antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins and healthy fats.
Eating a balanced diet can help to boost the immune system and reduce inflammation, which can help to improve skin health.
Also, some studies have suggested that certain nutrients may be beneficial for vitiligo, such as omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin B12, vitamin D and zinc.
It is always best to speak to your doctor or nutritionist before making any major dietary changes. An informed health decision based on professional medical advice is the best option.
If you have a question related to this blog post, write to us here and we will update this post with a response.
Sources: Mayo Clinic, Cleveland Clinic, NHS, NIAMS (1, 2), AAD, Medline Plus, Medical News Today (1, 2), Everyday Health, WebMD (1, 2), NIH, Vitiligo Clinic & Research Center, Healthline.
If you have any more questions, please feel free to write to us at support@nugenomics.in or call us directly at +91 9176655912
You can also visit Here to know more about how we can help you and make your life better.
 Cart is empty
Cart is empty 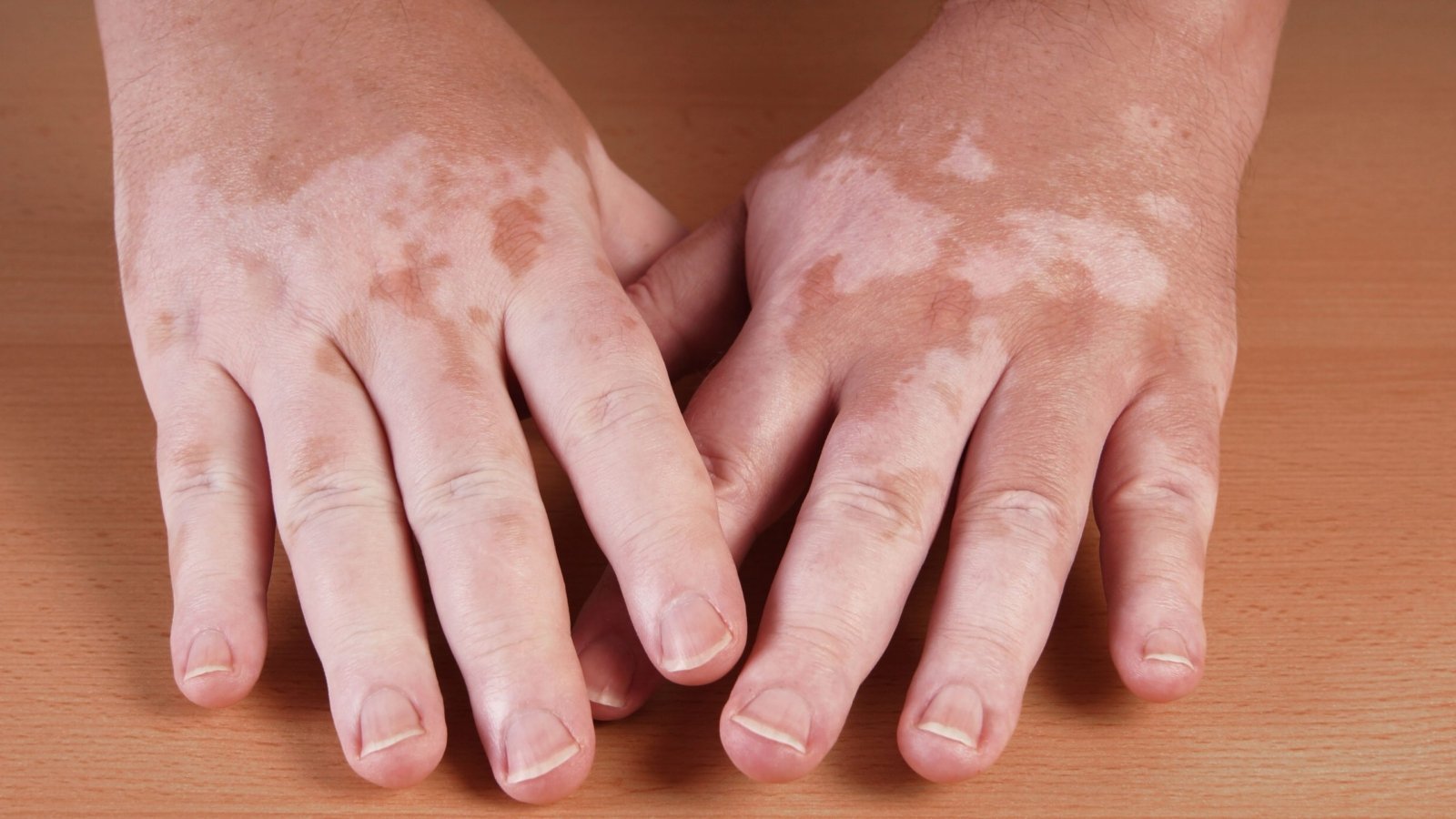
Add a Comment